How and when to apply potash fertilizers?
To increase the yield and quality of products, gardeners use potash fertilizers containing only potassium or with the addition of other elements. Most often these are water-soluble salts that are easily absorbed by plants. The correct choice of potassium-containing top dressing depends on the plant species, soil type and application time.
The importance of potassium for plants
In their life, plants most of all use three chemical elements: potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus. Cell sap and cytoplasm are the location of potassium in the plant organism, where it is concentrated mainly in young shoots. A sufficient amount of the element is especially important during the period of development and ripening of fruits, because potassium is indispensable in stabilizing metabolic processes:
- accelerates metabolism, carbon and nitrogen metabolism, improves photosynthesis;
- promotes the development of the root system and the creation of fruits of the correct shape;
- establishes water balance in such a way that plants do not suffer from drought, fully using the moisture reserve in the soil;
- with the participation of potassium, monosaccharides are converted into polysaccharides, sweetness accumulates in fruits, starch in potatoes;
- potassium is also responsible for plant aromatization;
- fruits that did not experience a lack of potassium during the formation process are stored longer;
- promotes the adaptation of plants to low temperatures due to the accumulation of sugars;
- helps to increase susceptibility to pathogens of various diseases: powdery mildew, rust, rot.
Signs of potassium deficiency
Potassium promotes the development of fruits, therefore, fruit and vegetable plants are in great need of it.
Obvious signs of a lack of an element are visible when its rate is reduced by 3 times:
- plants do not develop well, stems are thin;
- the border of the leaves is yellow and dry, the leaf blades are yellow or bluish-bronze, wrinkled, twisted, with deep veins;
- poor bud and ovary formation, small fruits;
- brown spot disease.
On average, 250 kg of potash fertilizers are needed per hectare for the normal growth of vegetables.
Potassium content in soils
Potassium is not found in sufficient quantities in all soils. Most of all, heavy soils are rich in this element. In clay soils and loams, its amount is usually 3%. A lack of potassium can be traced on light soils - up to 0.05%, especially plants in peat bogs suffer from its lack.
Potassium is in the top layer of the soil, but plants can assimilate only 10% of the substance, the rest is contained in poorly soluble compounds. Therefore, for a high yield, you need to apply potash fertilization. Their importance is important for increasing the productivity of agricultural plots. All species are available in a readily water-soluble form and are well absorbed by plants.
Types of potassium-based dressings
Potash preparations are produced from fossil ores that contain chlorides and sulfur. They use natural fertilizers and chemical by-products. The most commonly used natural salts for the production of dressings are chenite, langbeinite, sylvinite - they contain up to 25% potassium.
The finished fertilizers contain various additives that increase the efficiency of their use: chlorine, sulfur, magnesium and others. Not all preparations can be used for all crops, on different types of soils; there are recommendations for the period of their application. The potassium content is calculated as its oxide (K2O).
- Potassium chloride
The fertilizer contains 63% potassium and about 40% chlorine.In appearance, these are grayish-white or pink crystals that quickly moisten and cake if not stored properly. The drug is used for autumn fertilization, because many plants suffer from a large amount of chlorine - potatoes, tomatoes, cucumbers, beans, indoor flowers, grapes, buckwheat, tobacco. Spinach and celery respond well to this dressing. The substance also accumulates salts in the soil and increases its acidity. Potassium chloride is not used on heavy soils.
- Potassium sulfate
Another common name is potassium sulfate... The preparation contains up to 50% potassium oxide, it also contains sulfur, calcium and magnesium. The substance in the form of small yellowish crystals absorbs little water, it is easier to transport and store. It is widely used in greenhouses, for crops that cannot tolerate forms with chlorine. Cruciferous and legumes need to be fed with potassium sulfate, since they need sulfur. Potassium sulfate is applied at any time and on almost all soils (except for acidic soils, where acidity increases with its use). Also, the drug is not mixed with lime substances.
In the presence of sulfur, plants accumulate less nitrates. Therefore, potassium sulfate is useful for feeding vegetables.
- Kalimagnesia
It is also a chlorine-free preparation - a gray-pink powder. It is brought into the area with tomatoes, potatoes and other vegetables. The content of 29% potassium and 9% magnesium makes the fertilizer desirable for plants on sandy loam and sandy soils, poor in these elements. The powder is not hygroscopic, does not cause problems during transportation and storage.
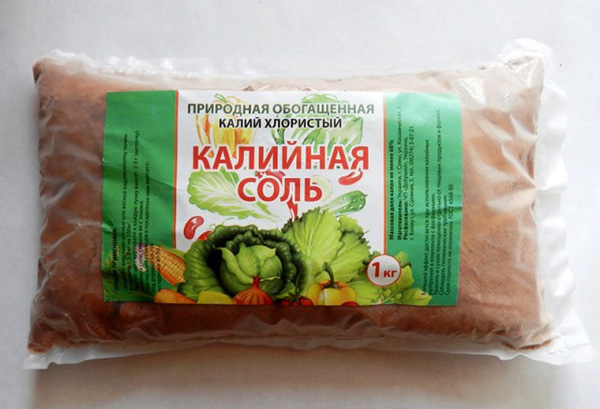
- Potassium salt
In appearance, these are small crystals of grayish, white or pink color. There are 40% and 30% salt (corresponding to the potassium content). The rest of the substance is chlorine. Fertilizer is not used for vegetables and other crops that cannot tolerate chlorine. Suitable for sugar beets and fodder root crops, as it contains the sodium they need. In the correct dosage, according to the instructions, potassium salt is necessary for fruit and berry plants.
There is magnesium in 30 percent salt. The drug is applied on light sandy and peaty soils during autumn work. Potassium salts can be applied in spring on wet soils - chlorine will be washed out of them, and potassium will be fixed. In summer, these dressings are not used.
- Potassium carbonate
Chlorine-free fertilizer is also known under the names of potassium carbonate and potash. The substance quickly cakes, the damp loses its quality. Lime is added to it, which leads to alkalization of the soil, or peat. Suitable for acidic soils.
- Cement dust
This compound is rich in potassium: 10-35%. Introduced for plants that react poorly to chlorine. It increases the alkali content in the soil, therefore it is used to neutralize acidic soils.
A popular natural supplement with potash and phosphorus. The amount of potassium depends on the type of wood being burned. Ash with 14% potassium is obtained from young deciduous trees. The ash of conifers and old trees contains less of it. Good fertilizer for acidic soils.
Ash is not mixed with poultry droppings and manure, superphosphate and nitrogen preparations.
Complex and mixed tuk
With the development of technologies, various substances are easily mixed and processed, therefore, complex forms of mineral fertilizers: double and triple, are widely recognized. Produce and use nitrogen-potash, phosphorus-potash, nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium preparations. Dry and liquid forms of complex preparations with a balanced set of substances for one particular culture are now popular.
- Potassium nitrate
The product in the form of small yellowish-gray crystals contains 46% potassium and 13% nitrogen. It can harden and become unusable in high humidity. Store only in a dry place. Saltpeter stimulates the development of crops, is introduced at planting, as well as in summer. It is used on neutral soil, since potassium is not assimilated on alkaline ones, and nitrogen on acidic ones.
The balanced fertilizer contains equally nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium oxides. It is brought in in the fall, as well as root dressing in spring and summer.
- Potassium monophosphate
A beige potassium-phosphorus preparation, which is better for a personal plot in granular form. It contains 28% potassium, 23% phosphorus. Good fertilizer for vegetables and flowers: stimulates fruiting, increases resistance to diseases, causes violent growth of lateral shoots. Often used in greenhouses, outdoors for vegetables, balcony flowers.
Features of the introduction of potassium preparations
Before using the funds, you must carefully read the instructions.
- It is recommended to apply potash fertilizers in autumn on heavy clay soils, and on light soils in spring.
- Potash fertilizers are best applied in small portions.
- Potassium is better absorbed by plants if fertilized on moist soil in cool weather.
- In spring, potassium is used in mixtures more than nitrogen. In autumn, the amount of nitrogen is increased.
- The correct dosage of potassium is important for tomatoes, which helps the plant to form beautiful and tasty fruits. A green spot near the stalk is a sign of a lack of potassium.
- For potatoes, potash fertilizers are used without chlorine.
The drugs will be beneficial when used correctly. Root dressing is especially effective in the ovary creation phase.











Thank you for a very instructive article.